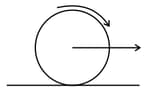
Rolling Motion
Rolling Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Rolling Motion of a Rigid Body, Pure and Impure Rolling Motion, Velocity of Points in Rolling, Pure Rolling, Forward Slip and Backward Slip and Angular Momentum of a Rigid Body in Rolling.
Important Questions on Rolling Motion
These questions consists of two statements each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions you are required to choose any one of the following five responses.
Assertion: A solid sphere cannot roll without slipping on smooth horizontal surface.
Reason: If the sphere is left free on smooth inclined surface, it cannot roll without slipping.
A uniform solid cylindrical roller of mass is being pulled on horizontal surface with force parallel to the surface applied at its centre. If the acceleration of the cylinder is and it is rolling without slipping, then the value of is
A uniform solid ball of mass '' rolls without sliding on a fixed horizontal surface. The velocity of the lowest point of the ball with respect to the center of the ball is . The total kinetic energy of the ball is:
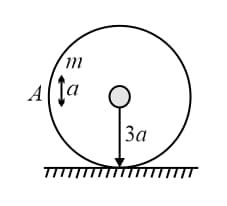
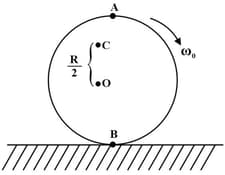
A ring of radius is fixed rigidly on a table. A small ring whose mass is and radius rolls without slipping inside it as shown in the figure. The small ring is released from position . When it reaches the lowest point, the speed of the centre of the ring at that time would be,
In rotational motion of a rigid body, all particles move with _____.
What is the ratio of total kinetic energy and translation kinetic energy of rolling body of radius and radius of gyration ?
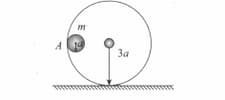
A ring of radius is fixed rigidly on a table. A small ring whose mass is and radius , rolls without slipping inside it as shown in the figure. The small ring is released from position . When it reaches the lowest point, the speed of the centre of the ring at that time would be
A wheel moving down a perfectly frictionless inclined plane will undergo slipping (not rolling) motion.
For perfect rolling motion, work done against friction is zero.
The instantaneous acceleration of the point of contact during rolling is zero.
During rolling, the force of friction acts in the same direction as the direction of motion of the centre of mass of the body.
A disc of radius is rotating with an angular about a horizontal axis. It is placed on a horizontal table. The coefficient of kinetic friction is . Calculate the time taken for the rolling to begin.
A solid cylinder and a hollow pipe of same diameter are in contact when they are released from rest as shown in the figure on a long incline plane. Cylinder and pipe roll without slipping. Determine the clear gap (in ) between them after seconds.
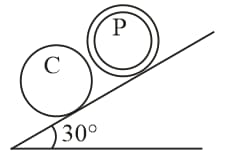
A solid ball of mass and radius spinning with angular velocity falls on a horizontal slab of mass with a rough upper surface (coefficient of friction ) and a smooth lower surface. Immediately after the collision, the normal component of the velocity of the ball remains half of its value just before the collision and it stops spinning. Find the velocity of the sphere in the horizontal direction immediately after the impact (given: ).
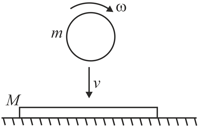
A uniform ball of radius rolls without slipping between two rails such that the horizontal distance is between two contact points of the rail to the ball. If the angular velocity is , then find the velocity of centre of mass of the ball in .
A solid sphere rolls on a rough horizontal surface with a linear speed 7 m/s collides elastically with a fixed smooth vertical wall. Then the speed of the sphere when it has started pure rolling in the backward direction in m/s is.
A point is located on the rim of wheel of radius which rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface then the total distance(in ) traversed by the point in meters between two successive moments it touches the surface is
A disc rotating about its axis with angular speed is placed lightly (without any translational push) on a perfectly frictionless table. The radius of the disc is . Let and be the magnitudes of linear velocities of the points and on the disk as shown. Then,
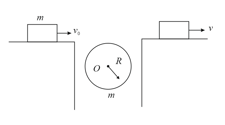
A block of mass m moves with a velocity on a smooth horizontal surface. It then passes over a solid cylinder of radius and mass m, capable of rotating about its own fixed axis through The block, while passing over, slips on the cylinder. The slipping stops before it loses contact with cylinder. The block then moves on a similar smooth horizontal surface with a velocity . Then the velocity is
A bicycle wheel rolls without slipping on a horizontal floor. Which one of the following is true about the motion of points on the rim of the wheel, relative to the axis at the wheel's centre?